manual fuel pump
Manual fuel pumps are basic, portable devices designed to transfer fuel without electricity․ They are essential for emergencies, remote locations, and small engine fueling, offering reliability and simplicity․
1․1 Overview of Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps are portable devices designed for transferring fuel without electricity․ They include rotary, lever, and siphon styles, compatible with fuels like gasoline, diesel, and kerosene․ Built for durability, these pumps offer efficient, reliable operation, making them ideal for low-volume fueling needs in remote or off-grid locations where power is unavailable․ They ensure safe and controlled fuel transfer․
1․2 Importance of Manual Fuel Pumps in Fuel Transfer
Manual fuel pumps are crucial for transferring fuel in remote or off-grid locations where electricity is unavailable․ They offer portability, reliability, and versatility, making them ideal for emergencies, small engines, and low-volume fueling needs․ Their simplicity ensures safe and controlled fuel transfer, reducing spillage and environmental risks while providing a cost-effective solution for various applications․

Types of Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps come in various designs, including rotary, lever-operated, and siphon-style models․ Each type offers unique benefits, such as portability, ease of use, and durability, catering to different fuel transfer needs․
2․1 Rotary Manual Fuel Pumps
Rotary manual fuel pumps operate with a rotating handle, offering efficient fuel transfer․ They are durable, ideal for high-volume needs, and often used in industrial settings․ Their robust design ensures long-term reliability and consistent performance across various fuel types, making them a popular choice for heavy-duty applications․
2․2 Lever-Operated Manual Fuel Pumps
Lever-operated manual fuel pumps use a simple, ergonomic lever mechanism for fuel transfer․ They are easy to operate, suitable for various fuels, and ideal for low to moderate flow rates․ Their compact design and reliability make them popular for small engines, remote locations, and applications requiring portability and ease of use․
2․3 Siphon-Style Manual Fuel Pumps
Siphon-style manual fuel pumps use a combination of suction and gravity to transfer fuel․ They are lightweight, portable, and require minimal effort, making them ideal for small-scale fueling needs․ These pumps are often used for transferring gasoline, diesel, or other liquids in applications where simplicity and ease of use are prioritized․

Key Features of Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps are known for their efficiency, durability, and portability․ They often feature adjustable flow rates and are designed for ease of use in various environments․
3․1 Flow Rate and Efficiency
Manual fuel pumps ensure steady fuel transfer with varying flow rates, such as 3․2 gallons per minute․ Their efficiency minimizes spillage and saves time, making them ideal for low to moderate fueling needs in diverse environments․
3․2 Material and Durability
Manual fuel pumps are constructed from durable materials like cast iron, heavy-duty plastics, and stainless steel, ensuring longevity and resistance to corrosion․ These robust designs withstand rigorous use in harsh environments, making them reliable for long-term fuel transfer applications․
3․4 Portability and Ease of Use
Manual fuel pumps are designed for portability, featuring lightweight and compact designs that allow easy transport․ Their straightforward operation requires minimal effort, with handles or levers for simple pumping․ Flexible suction hoses and easy-to-use nozzles enhance convenience, making them ideal for on-the-go fuel transfer in remote or off-grid settings․

How to Choose the Right Manual Fuel Pump
Selecting the right manual fuel pump involves evaluating compatibility with your fuel type, required flow rate, and build quality to ensure reliability and durability for your needs․
4․1 Consider Fuel Type and Compatibility
Ensure the pump matches your fuel type, such as gasoline, diesel, or kerosene, and is compatible with the container material․ Choose pumps made from materials like plastic, metal, or stainless steel, suitable for your fuel and application to prevent corrosion and ensure safe, efficient transfer․
4․2 Determine the Required Flow Rate
Assess the flow rate needed based on your fueling requirements․ Manual pumps vary in capacity, from 3․2 to 20 gallons per minute․ Higher flow rates suit larger applications, while lower rates are ideal for smaller, precise transfers․ Ensure the pump’s flow rate aligns with your specific needs for efficient and effective fuel transfer․
4․3 Evaluate the Pump’s Build Quality
Assess the pump’s build quality by checking materials like stainless steel or cast iron for durability․ Ensure the pump is compatible with your fuel type and can withstand harsh environments․ Look for heavy-duty construction and corrosion-resistant components to ensure long-term reliability and performance in demanding conditions․

Installation and Maintenance of Manual Fuel Pumps
Proper installation involves following manufacturer guidelines, while regular maintenance ensures longevity․ Clean the pump, check for wear, and store it securely to maintain optimal performance and safety․
5․1 Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Begin by positioning the pump near the fuel source․ Attach the suction hose to the inlet port and the discharge hose to the outlet․ Secure all connections tightly․ Ensure the pump is placed on a stable surface․ Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for priming the pump․ Test the pump at a low flow rate to check for leaks or issues before full operation․
5․2 Regular Maintenance Tips
Regularly inspect the pump for wear and tear․ Clean the suction and discharge hoses to prevent blockages․ Lubricate moving parts to ensure smooth operation․ Check for leaks and tighten connections as needed․ Store the pump in a dry, protected area when not in use․ Replace worn or damaged seals to maintain efficiency and prevent fuel leaks․
5․3 Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues include low flow rate, air entering the system, or blockages․ Check for kinked or clogged hoses and ensure all connections are tight․ If the pump fails to prime, inspect the suction hose for obstructions․ Replace worn-out seals or O-rings to prevent leaks․ Regular cleaning and lubrication can resolve most operational problems effectively․

Safety Precautions When Using Manual Fuel Pumps
Always wear protective gear, ensure good ventilation, and avoid sparks․ Keep flammable liquids away from heat sources and follow manufacturer guidelines to prevent accidents and spills․
6․1 Handling Flammable Fuels Safely
When handling flammable fuels, always wear protective gear and ensure the area is well-ventilated․ Avoid sparks, static electricity, and open flames․ Use approved containers with tight seals to prevent spills and vapors․ Ground equipment to prevent static buildup and keep emergency equipment nearby, such as fire extinguishers, to address potential accidents quickly and effectively․
6․2 Avoiding Overfilling and Spillage
To prevent overfilling and spillage, always monitor the fuel level during transfer․ Use pumps with automatic shut-off or built-in overflow protection․ Ensure containers are placed on level ground and have tight-fitting lids․ Avoid pumping too quickly, and keep absorbent materials handy to contain minor spills․ Regularly inspect hoses and connections for leaks before use․
6․3 Proper Storage and Handling
Store manual fuel pumps in a dry, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and flammable materials․ Keep them clean and lubricated to maintain functionality․ Handle pumps with care to avoid damage, and ensure all components are securely attached before use․ Regularly inspect for wear and tear, and follow manufacturer guidelines for storage and maintenance․

Popular Brands and Models of Manual Fuel Pumps
Fill-Rite, TERA Pump, and GPI are leading brands offering reliable manual fuel pumps․ Models like Fill-Rite FR152 and TERA Pump TRM20 are known for durability and efficiency․
7․1 Fill-Rite Manual Fuel Pumps
Fill-Rite manual fuel pumps are renowned for their durability and reliability․ The FR152 model features heavy-duty construction, making it ideal for transferring diesel, gasoline, and other fuels efficiently․ Known for their long-lasting performance, Fill-Rite pumps are a preferred choice for both industrial and personal use, ensuring safe and consistent fuel transfer operations․
7․2 TERA Pump Manual Fuel Transfer Pumps
TERA Pump Manual Fuel Transfer Pumps, like the TRM20 model, offer efficient fuel transfer without electricity․ They pump up to 3․2 gallons per minute, reducing spillage with a flexible suction hose․ Durable and portable, these pumps are ideal for gasoline, diesel, and kerosene, making them a reliable choice for various fueling needs in different settings․
7․3 GPI Manual Fuel Transfer Pumps
GPI manual fuel transfer pumps are known for their durability and efficiency․ The 20 GPM 12V model features an automatic diesel nozzle, ensuring quick and reliable fueling․ Built for longevity, GPI pumps handle various fuels, including diesel and gasoline, making them a versatile choice for diverse applications and user needs․
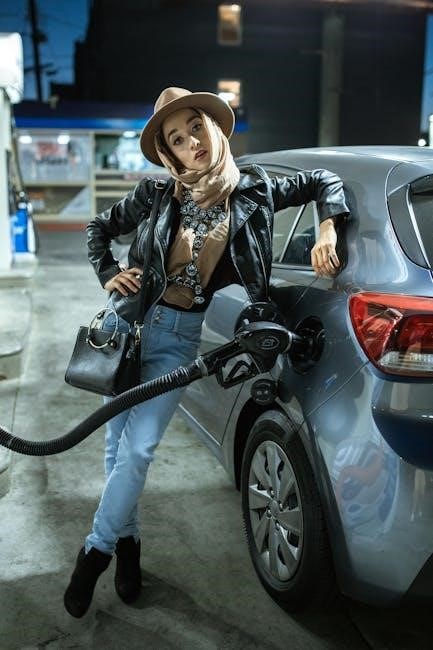
Applications of Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps are ideal for fueling small engines, transferring diesel, gasoline, and other fuels, and are essential in remote or off-grid locations where electricity is unavailable․
8․1 Fueling Small Engines and Equipment
Manual fuel pumps are perfect for fueling small engines like lawnmowers, generators, and boats․ They provide a portable and efficient way to transfer fuel, ensuring equipment runs smoothly without electricity, making them ideal for home use and outdoor activities․
8․2 Transfer of Diesel, Gasoline, and Other Fuels
Manual fuel pumps efficiently transfer diesel, gasoline, and other fuels between containers․ Their durability ensures safe handling of flammable liquids, while flexible hoses and compact designs make them versatile for various applications, including automotive and industrial use․
8․3 Use in Remote or Off-Grid Locations
Manual fuel pumps are ideal for remote or off-grid locations where electricity is unavailable․ Their portability and ease of use make them essential for fueling generators, vehicles, and equipment in isolated areas․ Durable designs ensure reliability in harsh environments, providing a practical solution for fuel transfer without reliance on external power sources․

Advantages and Disadvantages of Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps offer portability, no electricity requirements, cost-effectiveness, and easy maintenance but are limited by slow flow rates and physical effort needed․
9․1 Benefits of Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps are portable, cost-effective, and require no electricity, making them ideal for remote areas․ They are easy to maintain, durable, and suitable for low-volume fueling needs, ensuring reliable performance in various environments without the dependency on power sources, thus offering a practical solution for emergency and off-grid situations․
9․2 Limitations of Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps are labor-intensive and time-consuming, requiring physical effort for operation․ They have limited flow rates, making them unsuitable for high-volume needs․ Additionally, they are less efficient for large-scale fuel transfer and may not be practical for prolonged or heavy-duty applications, limiting their use in industrial or high-capacity scenarios․
Manual fuel pumps are reliable, portable tools ideal for small-scale fuel transfer in remote or low-volume situations, offering simplicity and efficiency despite their labor-intensive operation․
10․1 Final Thoughts on Manual Fuel Pumps
Manual fuel pumps are reliable, portable tools for transferring fuel in various situations, especially where electricity is unavailable․ They offer simplicity and efficiency, making them ideal for small-scale use․
While labor-intensive, their durability and versatility across different fuels make them indispensable for emergencies, remote locations, and small engine fueling, ensuring convenient and safe fuel management․
10․2 Recommendations for Future Use
For future use, consider investing in durable, high-quality manual fuel pumps like Fill-Rite or TERA Pump․ Regular maintenance and proper storage ensure longevity․ Always follow safety guidelines and choose pumps compatible with your fuel type․ Manual pumps remain indispensable for small-scale, remote, or emergency fueling needs, offering reliability and efficiency․










Leave a Comment